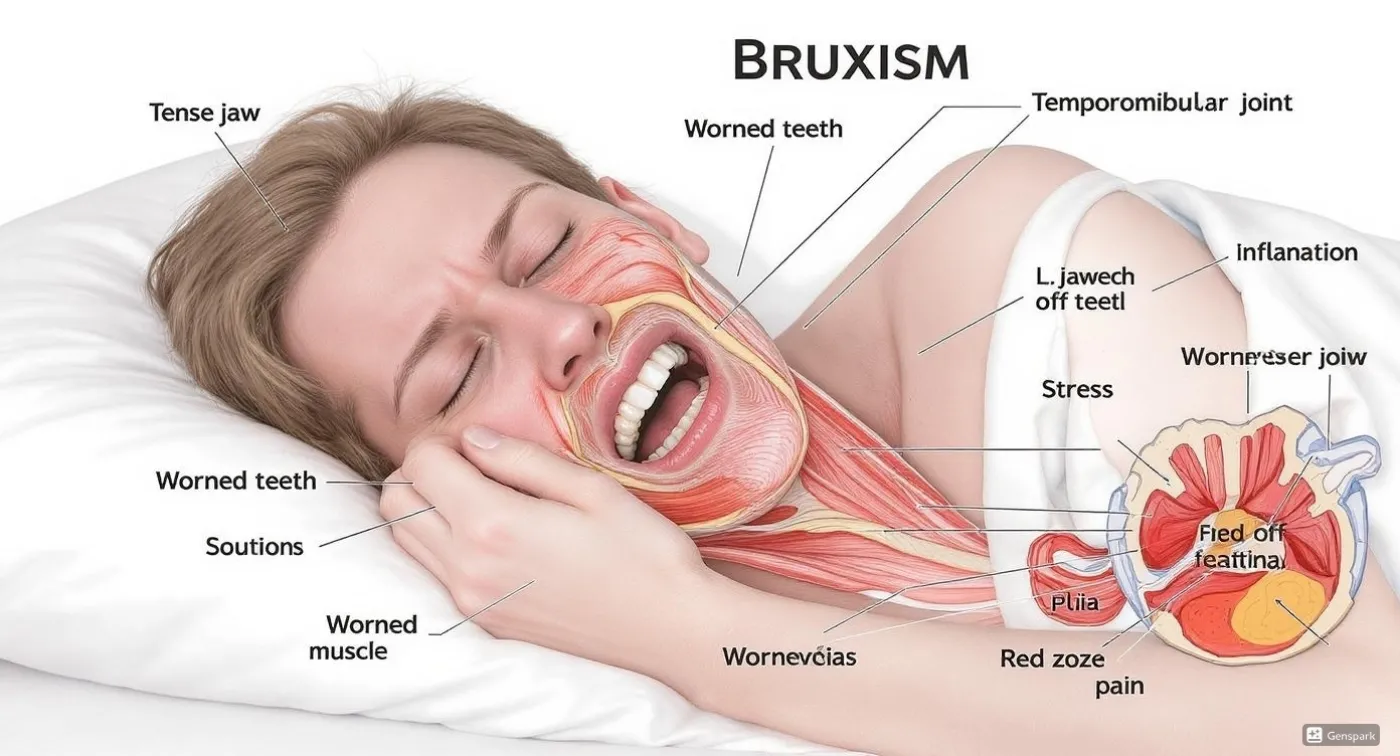
Bruxism is an involuntary jaw clenching and teeth grinding, affecting about 15% of adults and up to 50% of children. Causes: stress, incorrect bite, illnesses. Symptoms: jaw pain, enamel wear, headache. Diagnosis: examination, electromyography, polysomnography. Treatment: mouthguards, botulinum therapy, psychotherapy. Do not ignore it – consult specialists!
Bruxism (Teeth Grinding) and How to Get Rid of It Forever
Bruxism is not just a strange habit or occasional teeth grinding during sleep. In reality, this symptom reflects a serious disorder that requires medical attention. According to estimates, nearly 15% of the adult population suffers from this condition. Children also often grind their teeth.
The seriousness of this symptom should not be underestimated. Bruxism is associated with many hidden dangers - from damaged teeth to a general decline in quality of life. Fortunately, it is entirely possible to get rid of this problem and comprehensive therapy using modern methods makes it achievable.
What is Bruxism: Medical Definition and Types
Before discussing how to treat bruxism, it is important to understand what this pathology is and its characteristics.
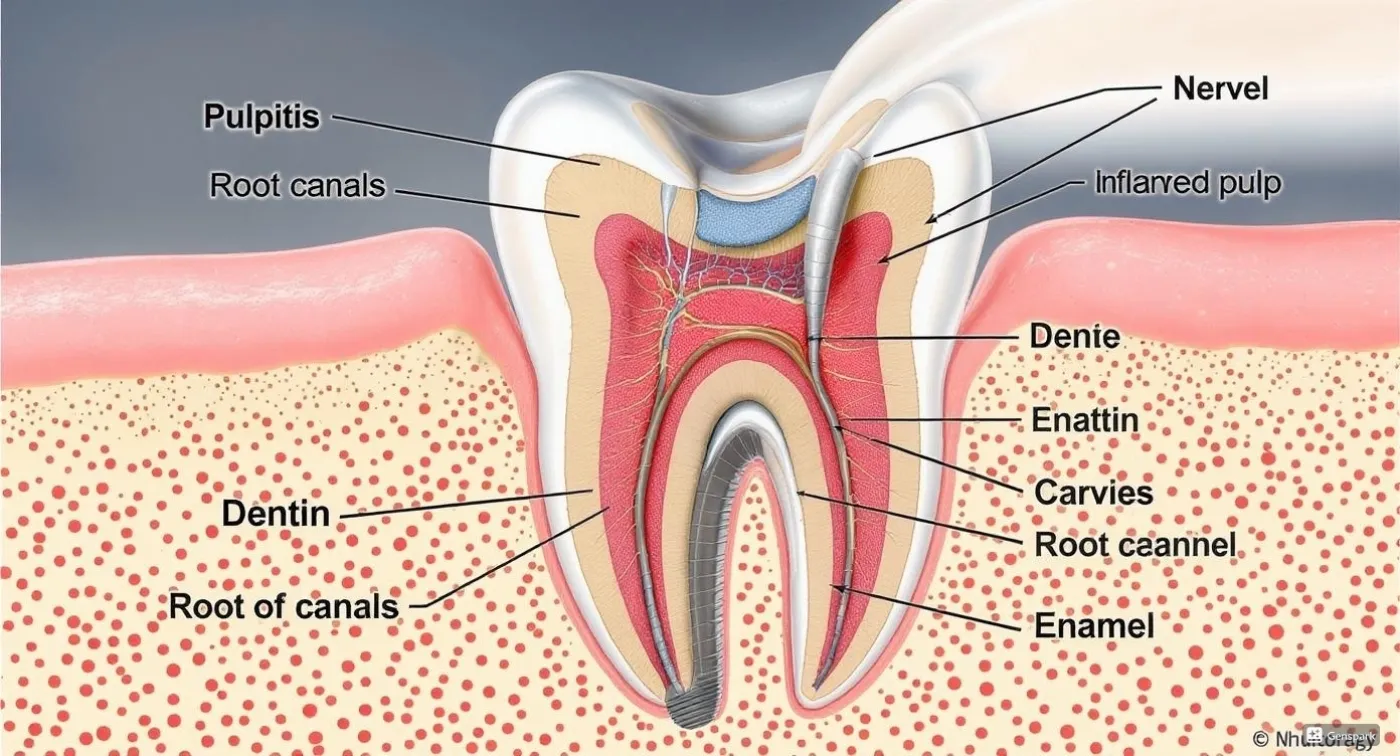
In medicine, bruxism, or odonterism, is defined as a condition characterised by involuntary clenching of the jaws and teeth grinding. Importantly, all this happens uncontrollably, without conscious effort. Grinding most often occurs during sleep, which is called nocturnal bruxism. However, uncontrolled grinding can also happen during the day, for example, when a person is nervous or thinking intensely.
This disorder is more commonly diagnosed in children - almost half of them. It occurs less frequently in adults but is harder to treat. Among adults, odonterism mostly affects people aged 25-44.
Types of Bruxism
In medicine, there are two types of bruxism:
- Primary, or idiopathic: Not associated with other diseases; occurs when teeth involuntarily clench or grind without any obvious cause;
- Secondary, or symptomatic: Develops against the background of certain diseases (e.g., Parkinson’s disease) or as a side effect of certain medications.
Additionally, childhood odonterism is distinguished because its pathogenesis often differs from the disorder’s characteristics in adults. But more on that later.
Main Causes of Bruxism: From Stress to Genetics
When discussing the causes of bruxism, several factors are usually highlighted:
- Psychological - there is a direct link between stress and bruxism; depressive states, emotional overload, and anxiety disorders can also trigger symptoms.
- Dental - misaligned bite, missing teeth (edentulism), overly crowded teeth, poorly fitting dentures or fillings that lead to incorrect tooth contact and tension in the jaws.
- Medical - jaw muscle spasms may occur with Parkinson’s disease, sleep disorders (such as apnea), or as side effects of antidepressants and certain stimulants.
- Lifestyle - smoking, alcohol or drug use, excessive caffeine consumption, and irregular sleep patterns.
A genetic predisposition to grinding and involuntary jaw clenching can be inherited. Contrary to popular myth, nighttime teeth grinding in adults or children is not related to parasites.
How to Recognise Bruxism: Symptoms and Diagnostic Methods
Bruxism in adults and children most often manifests as teeth grinding during sleep. There are also less obvious signs that may indicate this disorder:
- Morning jaw pain and discomfort while chewing;
- Increased tooth sensitivity;
- Tooth enamel wear, teeth may look shorter than before;
- Headaches, migraines, and neck tension.
Bruxism can also cause tooth loosening and damage, chronic jaw muscle spasms, and temporomandibular joint problems.
To avoid complications, it is essential to consult a dentist at the first suspicion of the disorder to assess the jaw system and obtain an accurate diagnosis. Modern dental clinics, including Gallant, use a comprehensive approach.
In addition to clinical examination, diagnostic methods such as electromyography and polysomnography may be used. Electromyography detects excessive muscle tone, while polysomnography assesses the activity of various body systems during sleep. Specialised diagnostic mouthguards called Brux Checker are also employed. They record the pressure on the jaw during sleep.
Effective Treatment of Bruxism: A Comprehensive Approach
Treatment of bruxism in adults and children is tailored individually by specialists based on diagnostic results. To achieve the best outcomes, a comprehensive approach combining several methods is usually applied:
Protective Mouthguards
The first recommendation for people with bruxism is protective mouthguards. These take on the main load during uncontrolled jaw clenching and prevent tooth enamel wear. Mouthguards can be soft, hard, or combined. The most effective are custom-made ones, created from dental impressions. For hygiene, the device should be cleaned regularly and stored in a special case. Mouthguards are relatively affordable, but should be replaced over time as they deform.
Dental Treatment
If dental factors are present, treatment may include bite correction, replacement of faulty fillings, tooth reshaping, or prosthetics for missing teeth.
Medication Therapy
Medication for bruxism may include muscle relaxants, sedatives, magnesium and calcium supplements that help with uncontrolled spasms. Sometimes antidepressants are prescribed.
Psychotherapy and Stress Management
If teeth grinding is caused by psychological factors, cognitive-behavioral therapy, meditation, yoga, and breathing exercises are recommended.
Physiotherapy
Manual therapy, massage of the chewing muscles, warm compresses, and therapeutic exercises can sometimes relieve symptoms. It is important that these procedures are performed by a physiotherapist experienced in working with the temporomandibular joint (TMJ).
Bruxism in Children: When to Be Concerned and How to Treat
In childhood, nighttime teeth grinding can have various causes and does not always require treatment.
Children’s bruxism is normal:
- up to 6-7 years old, while the nervous system is still developing;
- during teething;
- during periods of stress and adaptation to changes (moving house, starting kindergarten or school, etc.).
Bruxism requires treatment if it is accompanied by tooth damage, sleep disturbances, or if the child complains of headaches, pain in the jaw, or facial muscles. In such cases, a special children’s mouthguard may be recommended, along with work with a psychologist, adjusting the daily routine, and reducing stress factors.
How to Fight Bruxism at Home: Effective Methods
There are several ways to manage teeth grinding independently at home. Popular methods include:
- Relaxation techniques (yoga, self-massage, jaw relaxation exercises);
- Lifestyle changes (physical activity, establishing a sleep routine, limiting alcohol and caffeine);
- Creating comfortable sleeping conditions in the bedroom;
- Mindful control of jaw clenching during the day.
These are simple but effective tips that can complement a comprehensive treatment plan.
Prevention of Bruxism: How to Avoid the Problem
Bruxism prevention is divided into primary and secondary measures. Primary prevention focuses on maintaining a healthy psycho-emotional state, avoiding stress, and trying to reduce nervous tension. It is also important to lead a healthy lifestyle, have regular dental check-ups, and promptly treat any dental issues.
Secondary prevention involves early detection of bruxism symptoms to prevent future complications. If symptoms or risk factors are already present, using preventive mouthguards can help. The key is not to ignore the body’s warning signs.
When Professional Help for Bruxism Is Needed
If teeth grinding or uncontrolled jaw clenching occurs regularly, home remedies are ineffective, pain develops, or noticeable enamel wear appears, you should immediately consult a dentist. It is important to find not just a good dentist but a specialist experienced in diagnosing and comprehensively treating bruxism.
Modern Methods of Treating Bruxism
Treatment of bruxism in modern clinics, including Gallant Dental Clinic, goes beyond just protective mouthguards. Advanced technologies and innovative methods significantly improve patients’ quality of life.
Botulinum Therapy has proven to be highly effective. Botulinum toxin injections relax the chewing muscles responsible for nighttime jaw clenching. This reduces muscle spasm strength, helping to prevent tooth wear and pain. The therapeutic effect appears almost immediately after the injection and lasts for 4–6 months. Repeat injections can be done as needed. This method suits most adults except pregnant or breastfeeding women, allergy sufferers, and individuals with certain neurological conditions.
Digital Technologies also assist in treatment. There are special mobile apps for people with bruxism that periodically remind users during the day to relax their jaw muscles.
Smart Mouthguards with built-in pressure sensors are gaining popularity. They monitor the intensity and frequency of teeth grinding at night. The collected data helps tailor the treatment plan individually. Telemedicine is also on the rise, enabling patients to consult with doctors remotely and get treatment advice from Korosten, Kyiv, or any other region without visiting the clinic in person.
Summary: How to Successfully Overcome Bruxism
Bruxism is not a sentence but a signal that the body needs extra care. The earlier the problem is diagnosed, the easier it is to solve. Moreover, modern comprehensive treatment methods allow relief from pain and discomfort, restoration of quality sleep, and prevention of tooth damage.
Don’t ignore your body’s signals. Contact the specialists at Gallant Dental Clinic who know exactly how to help even in very complex cases of bruxism.
Request a call
We will contact you to schedule a convenient time for your consultation and connect you with the right specialist
More articles
We have gathered all the most interesting posts from our specialist doctors in our blog just for you
Dental Treatment During Pregnancy: Myths and Facts
Bruxism (Teeth Grinding) and How to Get Rid of It Forever


Request a call
We’ll get back to you shortly!

Leave a Review
Your feedback means a lot to us!