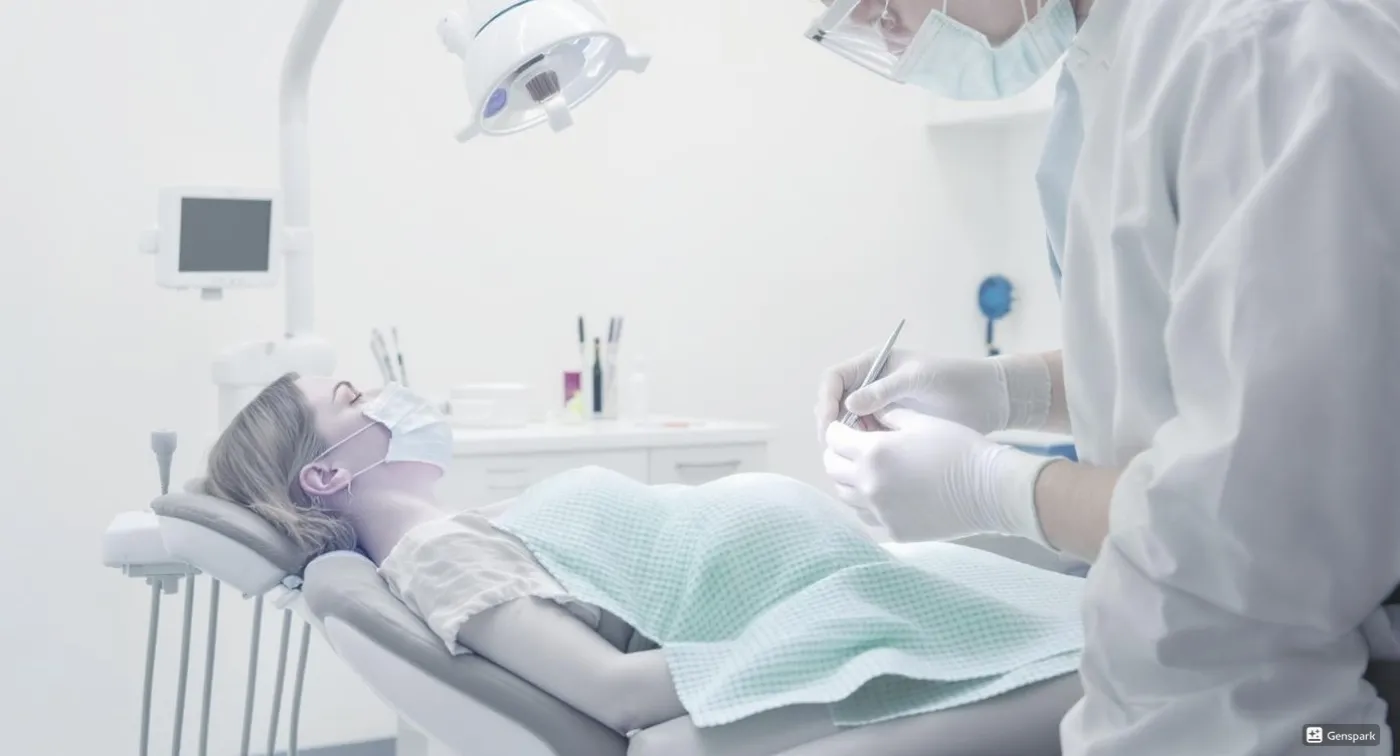
Dental health during pregnancy is essential for the wellbeing of both mother and baby. Modern dentistry is safe: treat cavities, get professional cleanings, and don’t fear anesthesia. Regular check-ups and proper hygiene help prevent complications. Visit us in Korsun or Horodyshche!
Dental Treatment During Pregnancy: Myths and Facts
Although pregnant women usually prioritise the health of their baby, it is equally important not to forget about their own wellbeing - especially dental health. During pregnancy, the body undergoes many changes, some of which can negatively affect the condition of the oral cavity.
According to statistics, nearly 70% of women experience gum inflammation and tooth decay during pregnancy. The danger lies in the fact that many still believe the myth that dental treatment during pregnancy is forbidden, and consider oral health issues during this time a normal part of motherhood - "a price to pay for becoming a mother."
It’s time to debunk the most common myths. Specialists at Gallant Dental Clinic explain in this article whether pregnant women can undergo dental treatment, whether local anaesthesia is allowed during pregnancy, and provide answers to the most frequently asked questions future mothers have about dental care.
How pregnancy affects the health of teeth and gums
During pregnancy, the female body undergoes major transformations. Many of these directly or indirectly impact oral health.
Hormonal changes and their consequences
Increased levels of oestrogen and progesterone affect the oral microbiome and enhance blood flow to the gums. As a result, the gums may swell, become sensitive and more vulnerable to bacteria, and may bleed even during normal brushing. This is the main reason for the frequent occurrence of pregnancy gingivitis.
Other bodily changes that affect the teeth
Throughout the entire period of fetal development, the baby forms its own skeletal system. If the mother’s diet lacks calcium, magnesium, phosphorus, and vitamin D, her body will draw these elements from its own tissues, including the teeth.
Due to hormonal changes, the pH and composition of saliva also shift, reducing its protective functions. This creates an ideal environment for bacterial growth in the mouth.
Toxicosis and vomiting also have a negative impact on teeth. Stomach acid present in vomit erodes tooth enamel and increases the risk of erosions and cavities.
Another less obvious reason for dental problems during pregnancy is the change in eating habits. Cravings for sweets or sour foods, frequent snacking, and late-night fridge visits all contribute to plaque buildup and increased dental risks.
Top 10 Most Common Myths About Dental Treatment During Pregnancy
Changes in the body during pregnancy already present serious challenges for dental health, and outdated myths only make things worse. Can pregnant women get dental treatment? Do painkillers and X-rays harm the baby? Let’s find out what modern medicine has to say.
Dental treatment is strictly forbidden during pregnancy
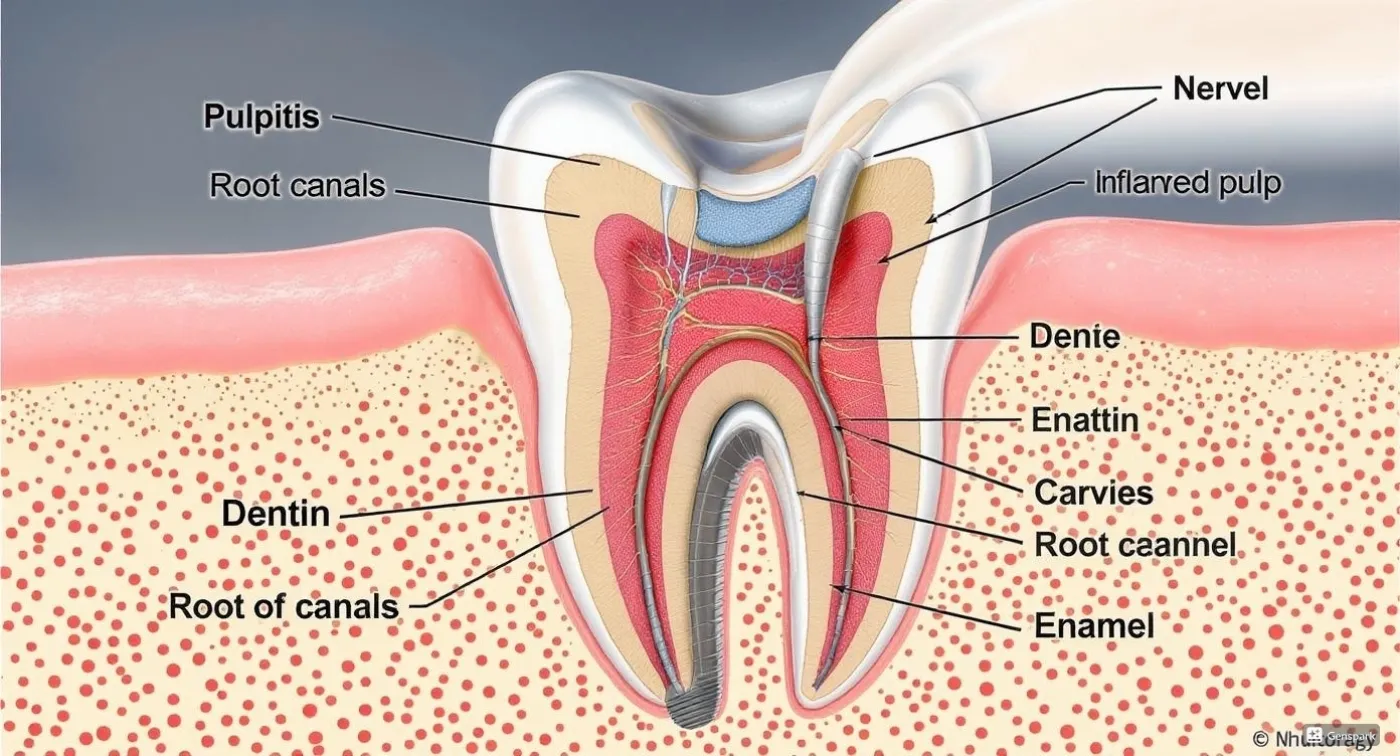
Fact: Not only is dental treatment allowed, it’s necessary. Untreated cavities, pulpitis, or periodontitis pose greater risks than treatment itself. The bacteria responsible for tooth decay trigger cytokine production, which can lead to uterine contractions and increase the risk of premature birth. Infections from decaying teeth can enter the bloodstream and affect the baby’s health and development.
Anaesthesia harms the baby
Fact: Modern dental anaesthesia for pregnant women works locally and does not cross the placenta. Today, pregnancy-safe anaesthetics based on articaine (without adrenaline) are used. These are approved for use during pregnancy. On the other hand, enduring dental pain is harmful — the stress hormones released can negatively affect the baby.
Dental X-rays are dangerous during pregnancy
Fact: Modern equipment emits minimal radiation. Dentists take targeted images, shielding the abdomen and thyroid. The radiation from a dental X-ray is lower than that of a typical flight. Digital radiovisiography and computer imaging reduce exposure even further.
Professional dental cleaning is not allowed
Fact: Proper oral hygiene is extremely important during pregnancy. Professional cleaning not only gently whitens teeth but also helps prevent gingivitis and cavities. The procedure is painless, done without anaesthesia, and is completely safe - even recommended every 3 months during pregnancy.
"A baby takes one tooth from the mother"
Fact: This old belief dates back to times when women lacked access to vitamins and dental care. Today, with proper nutrition and modern dentistry, it’s entirely possible to carry and deliver a healthy baby without losing teeth or damaging bone tissue.
All dental procedures are equally risky
Fact: Different procedures carry different levels of risk. Dentistry today includes preventive, diagnostic, therapeutic, and surgical treatments. Pregnant women don’t need to avoid all dental care so only certain treatments may need to be postponed.
Implants and prosthetics are forbidden
Fact: These are different procedures with specific considerations. Dental implants are best placed after birth, when the body is stronger and the risk of rejection is lower. However, prosthetics such as temporary crowns or bridges can be done during pregnancy, especially if the missing tooth affects eating or speaking.
Toothpastes with fluoride are harmful during pregnancy
Fact: Fluoride in safe amounts is beneficial during pregnancy. The key is to use a toothpaste with a dentist-approved fluoride concentration. Generally, formulas with 950–1150 ppm of fluoride are considered safe and effective.
Wisdom tooth removal is especially dangerous
Fact: The risks depend on the tooth’s position and condition. Planned removal of complex wisdom teeth is best postponed until after birth. Emergency extractions during pregnancy may be necessary in cases of pain, inflammation, infection, or abscess. In such cases, safe techniques and medications are used to protect the mother and baby.
Pregnant women should only use home remedies
Fact: Home remedies cannot replace modern medicine, especially for acute dental issues. Self-diagnosing and self-medicating can worsen the condition and lead to serious complications for both the mother and baby.
Dental Treatment During Different Trimesters of Pregnancy
When it comes to dental procedures during pregnancy, it's important to consider not only the nature of the treatment but also the timing. So, when is it safe for pregnant women to undergo dental care? Let’s break it down by trimester.
First Trimester (Weeks 1–12)
This is the critical period of organ formation in the fetus, so any non-urgent dental interventions should be postponed. However, if there is tooth pain, swelling, inflammation, or infection — treatment is necessary, but with enhanced safety precautions to protect both mother and baby.
Second Trimester (Weeks 13–28) – The "Golden Period"
By this stage, the placental barrier is fully formed, offering better protection for the fetus. This is the safest and most recommended time for routine dental care such as oral hygiene, professional cleaning, and cavity treatment. Local anaesthesia and dental X-rays are allowed, and some surgical procedures may also be performed if needed. So if you're wondering whether a tooth can be extracted during pregnancy - the second trimester is the best time for it, if necessary.
Third Trimester (Weeks 29–40)
Dental procedures during this period are generally avoided unless they are urgent. The reasons include the risk of preterm labour and physical discomfort due to the enlarged belly. However, each case is assessed individually, and emergency dental care is still provided with appropriate precautions.
Allowed and Prohibited Dental Procedures During Pregnancy
Often, expectant mothers avoid visiting the dentist out of fear of harming their baby. However, completely avoiding all dental treatments for the entire 9 months is not advisable. To protect both yourself and your child, it’s important to know when pregnant women can receive dental care and which procedures are permitted.
Allowed Procedures:
- Treatment of cavities with anesthesia, especially if the tooth is painful;
- Professional oral hygiene;
- Treatment of chronic gingivitis and acute gum inflammation;
- Emergency tooth extraction if the tooth is causing pain, infection, or inflammation;
- Filling cavities.
There are some procedures that are permissible during pregnancy but require special precautions. These include:
- Planned surgery - only if there is a risk of infection; the least risky surgical options are chosen;
- Teeth whitening - this procedure is avoided during the first weeks and in the last trimester of pregnancy because it involves potentially harmful bleaching agents for the fetus, and it also thins the enamel, which is already weakened during pregnancy;
- Orthodontic treatment - starting braces, aligners, or other orthodontic appliances is not recommended during pregnancy, but if a woman is already wearing braces, treatment can continue under medical supervision.
Prohibited Procedures:
- Implantation — this complex surgical procedure requires anesthesia, X-rays, and antibiotics, so it is best planned after breastfeeding is completed;
- General anesthesia — strictly contraindicated in dentistry during pregnancy;
- Therapy involving certain medications — many drugs are forbidden during pregnancy, so all prescriptions must be individualized and made by a healthcare professional.
Safe Anesthetics and Medications for Pregnant Women During Dental Treatment
Is it safe to use anesthetics when you have a toothache during pregnancy? Can pregnant women have a tooth extraction with an anesthetic injection? These are common questions that we will now answer.
Contrary to popular myth, painless tooth extraction during pregnancy is possible. For anesthesia, drugs with a composition safe for both the mother and the baby are used. Most often, this is articaine without adrenaline (Ultracain). It hardly penetrates the placenta and is quickly eliminated from the body. Meanwhile, popular lidocaine with adrenaline can only be used in extreme cases under strict medical supervision - there is a risk of vascular spasm.
To relieve acute tooth pain during pregnancy, paracetamol tablets can be used, which are considered safe for women. The main thing is not to exceed the recommended dose. It is better to avoid ibuprofen and antibiotics, especially in the third trimester. The best advice on what to take for toothache during pregnancy - effective and safe - will come from your doctor.
Prevention of Dental Problems During Pregnancy
During this period, it is more important than ever to use quality hygiene products and follow the correct toothbrushing technique: twice a day, with a soft toothbrush, avoiding excessive pressure on the gums. Dental floss and irrigators will also be helpful. In case of gum swelling, treatment is performed with agents prescribed by the doctor.
To maintain strong teeth, women should consume foods rich in calcium and vitamins while limiting sugar intake.
During pregnancy, it is necessary to visit the dentist at least twice - in the first and second trimesters - to detect problems at an early stage and begin treatment on time without pain or complications.
Of course, it is even better to take care of dental and oral health at the stage of planning pregnancy. Specialists recommend eliminating potential sources of infection, doing professional cleaning, filling cavities, and, if necessary, placing implants before conception.
If this was not done and a toothache, swelling, or another acute dental problem arises during pregnancy, do not delay visiting the doctor. Moreover, our dental clinic in Korsun and Horodyshche is always at your service.
Summary: Healthy Teeth = Healthy Pregnancy
There is no need to fear fillings, anesthesia, or professional teeth cleaning during pregnancy as modern dentistry is adapted to the special needs of pregnant women. Remember that infection in the oral cavity is a threat not only to the mother but also to the fetus.
By taking care of herself, a pregnant woman also cares for her child. And for this, very little is needed: regularly brush teeth, eat properly, and do not ignore scheduled dental check-ups.
Request a call
We will contact you to schedule a convenient time for your consultation and connect you with the right specialist
More articles
We have gathered all the most interesting posts from our specialist doctors in our blog just for you
Dental Treatment During Pregnancy: Myths and Facts

Bruxism (Teeth Grinding) and How to Get Rid of It Forever

Request a call
We’ll get back to you shortly!

Leave a Review
Your feedback means a lot to us!